之前学习爬虫的时候,如果是 HTML 的数据,通过 xpath 或是 css 选择器,就能很快的获取我们想要的数据,如果是 json 有没有类似 xpath 这种,能够直接根据条件定位数据,而不需要自行 json 解析在遍历获取。答案是有的,也就是 JSONPath。
在线测试网址 JSONPath 在线验证
所选用的环境是 Node + JavaScript,用到 jsonpath 这个包 jsonpath - npm (npmjs.com)
基本语法
过滤器表达式
通常的表达式格式为:[?(@.age > 18)] 表示当前节点属性 age 大于 18
| 操作符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
== | 等于符号,但数字 1 不等于字符 1(note that 1 is not equal to ‘1’) |
!= | 不等于符号 |
< | 小于符号 |
<= | 小于等于符号 |
> | 大于符号 |
>= | 大于等于符号 |
=~ | 判断是否符合正则表达式,例如[?(@.name =~ /foo.*?/i)] |
in | 所属符号,例如[?(@.size in [‘S’, ‘M’])] |
nin | 排除符号 |
size | size of left (array or string) should match right |
empty | 判空 Null 符号 |
语法就这些,不过单单有语法,不实践肯定是不够的。下面就是一些官方简单例子操作,还有一个终极实战
代码演示
var jp = require('jsonpath')
var cities = [
{ name: 'London', population: 8615246 },
{ name: 'Berlin', population: 3517424 },
{ name: 'Madrid', population: 3165235 },
{ name: 'Rome', population: 2870528 },
]
var names = jp.query(cities, '$..name')
// [ "London", "Berlin", "Madrid", "Rome" ]
如果使用 js 来遍历的话,也简单
let names = cities.map(c => c.name)
这个数据可能还没那么复杂,在看看下面这个例子,代码来源于https://goessner.net/articles/JsonPath
{
"store": {
"book": [
{
"category": "reference",
"author": "Nigel Rees",
"title": "Sayings of the Century",
"price": 8.95
},
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "Evelyn Waugh",
"title": "Sword of Honour",
"price": 12.99
},
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "Herman Melville",
"title": "Moby Dick",
"isbn": "0-553-21311-3",
"price": 8.99
},
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title": "The Lord of the Rings",
"isbn": "0-395-19395-8",
"price": 22.99
}
],
"bicycle": {
"color": "red",
"price": 19.95
}
}
}
| JsonPath | Result |
|---|---|
$.store.book[*].author | 所有 book 的 author 节点 |
$..author | 所有 author 节点 |
$.store.* | store 下的所有节点,book 数组和 bicycle 节点 |
$.store..price | store 下的所有 price 节点 |
$..book[2] | 匹配第 3 个 book 节点 |
$..book[(@.length-1)],或 $..book[-1:] | 匹配倒数第 1 个 book 节点 |
$..book[0,1],或 $..book[:2] | 匹配前两个 book 节点 |
$..book[?(@.isbn)] | 过滤含 isbn 字段的节点 |
$..book[?(@.price<10)] | 过滤price<10的节点 |
$..* | 递归匹配所有子节点 |
对应的语法可直接到在 JSONPath 在线验证网站上进行测试。要提一点的是,jsonpath 是支持使用 || 与 && 进行过滤的,比如上面要获取 category 为 fiction,price 大于 10 的语法为$..book[?(@.price>10 && @.category=="fiction")] 结果如下
[
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "Evelyn Waugh",
"title": "Sword of Honour",
"price": 12.99
},
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title": "The Lord of the Rings",
"isbn": "0-395-19395-8",
"price": 22.99
}
]
终极实战
也许你会觉得上面的例子太过简单了,可能没达到你预期所想要的效果,甚至还不如使用 json 遍历呢,下面我列举一个是我实战中遇到的例子(实际上这样的例子特别多),我先把部分数据展示出来(删除部分没用到的参数,实际参数远比这多),然后通过 js 遍历,以及 jsonpath 来获取我想要的数据。
结构
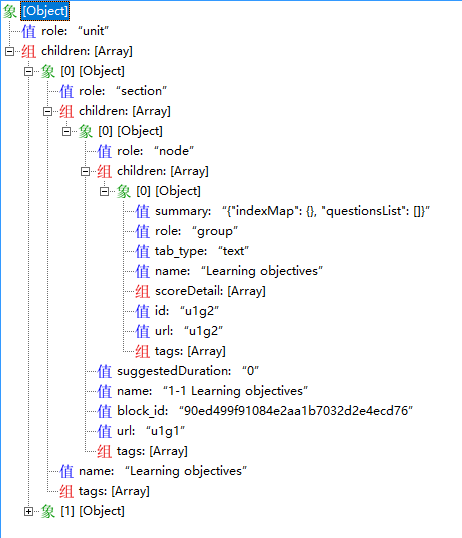
数据
{
"role": "unit",
"children": [
{
"role": "section",
"children": [
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"summary": "{\"indexMap\": {}, \"questionsList\": []}",
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "text",
"name": "Learning objectives",
"scoreDetail": [],
"id": "u1g2",
"url": "u1g2",
"tags": []
}
],
"suggestedDuration": "0",
"name": "1-1 Learning objectives",
"block_id": "90ed499f91084e2aa1b7032d2e4ecd76",
"url": "u1g1",
"tags": []
}
],
"name": "Learning objectives",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "section",
"children": [
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Practice-1",
"scoreDetail": [0],
"id": "u1g6",
"url": "u1g6",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Practice-2",
"scoreDetail": [1, 1, 1, 1],
"id": "u1g7",
"url": "u1g7",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Practice-3",
"scoreDetail": [1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
"id": "u1g544",
"url": "u1g544",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Practice-4",
"scoreDetail": [1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
"id": "u1g9",
"url": "u1g9",
"tags": []
}
],
"name": "Practice",
"block_id": "f6768dc9474746b9ba071e7f211534d9",
"url": "u1g5",
"tags": []
}
],
"suggestedDuration": "0",
"name": "1-2 Sharing",
"block_id": "1c97a87a9feb4a8aa7d6ed39482d866d",
"url": "u1g3",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "video",
"name": "Get the skills",
"scoreDetail": [],
"id": "u1g16",
"url": "u1g16",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Use the skills-1",
"scoreDetail": [0, 0],
"id": "u1g615",
"url": "u1g615",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Use the skills-2",
"scoreDetail": [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
"id": "u1g18",
"url": "u1g18",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Use the skills-3",
"scoreDetail": [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
"id": "u1g19",
"url": "u1g19",
"tags": []
}
],
"name": "Use the skills",
"block_id": "2d8a81799bcc44ccab2646b613557b2b",
"url": "u1g17",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Think and speak",
"scoreDetail": [0],
"id": "u1g21",
"url": "u1g21",
"tags": []
}
],
"name": "Think and speak",
"block_id": "5833925c8c5e4ddab7a114b15d610983",
"url": "u1g20",
"tags": []
}
],
"suggestedDuration": "0",
"name": "1-3 Listening",
"block_id": "681817aaf75845468e464e1a8d82f2c8",
"url": "u1g14",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Get a clue",
"scoreDetail": [0, 0, 0],
"id": "u1g25",
"url": "u1g25",
"tags": []
}
],
"name": "Get a clue",
"block_id": "b332335ab3554dffb92afcae5f815b5a",
"url": "u1g24",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "View it-1",
"scoreDetail": [1, 1, 1, 1],
"id": "u1g27",
"url": "u1g27",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "View it-2",
"scoreDetail": [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
"id": "u1g545",
"url": "u1g545",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "View it-3",
"scoreDetail": [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
"id": "u1g29",
"url": "u1g29",
"tags": []
}
],
"name": "View it",
"block_id": "a2ecf6464d5f480e98242ebe4431a73b",
"url": "u1g26",
"tags": []
},
{
"role": "node",
"children": [
{
"role": "group",
"tab_type": "task",
"name": "Think and speak",
"scoreDetail": [0, 0],
"id": "u1g31",
"url": "u1g31",
"tags": []
}
],
"name": "Think and speak",
"block_id": "120d0784e63c414793f5e648c416144b",
"url": "u1g30",
"tags": []
}
],
"suggestedDuration": "0",
"name": "1-4 Viewing",
"block_id": "765a1be83ac5437aaca8fa150ad5af2e",
"url": "u1g22",
"tags": []
}
],
"name": "Listening to the world",
"tags": []
}
]
}
需求
可以看到数据比一开始的例子复杂了可不是一点,不过先别管这些数据是干啥的,说说需求,从结构上也能看出来,是有很多children嵌套的,而需求就是获取role为group的children节点数据
js 实现遍历
先说说 js 如何实现的,我贴一下对应的代码(当时项目的代码,稍微修改的一点),可自己粘贴运行一下。
let groupList = []
for (const node of json.children ?? []) {
if (node.role == 'group') groupList.push({ ...node })
for (const group of node.children ?? []) {
if (group.role == 'group') groupList.push({ ...group })
for (const child of group.children ?? []) {
if (child.role == 'group') groupList.push({ ...child })
let children4 = child.children ?? []
for (const child of children4) {
if (child.role == 'group') groupList.push({ ...child })
}
}
}
}
console.log(groupList)
因为这些数据中,是存在不确定性的,也就是在当前节点下,二级节点可能有children,而其他节点下的二级很可能没有 children,所以我在这边就加上 ?? [] (Typescript 中的??语法,你可以把 ?? 当做 || )来判断是否有children节点,有些读者可能会思考,为啥不用递归呢。说的是挺轻松的,但是递归是很容易出问题的,万一爬取到后台数据进行了一些修改,很有可能对于的递归算法将失效,甚至导致堆栈溢出,所以我这边值循环 4 级chilren节点(实际遇到的貌似也只有 4 级,谁又能保证爬取到数据就一定只有 4 级呢)。
jsonpath 获取
于是了解到 jsonpath 后,我第一个时间就开始分析这样的数据,果不其然,得到了我想要的结果 ⬇️
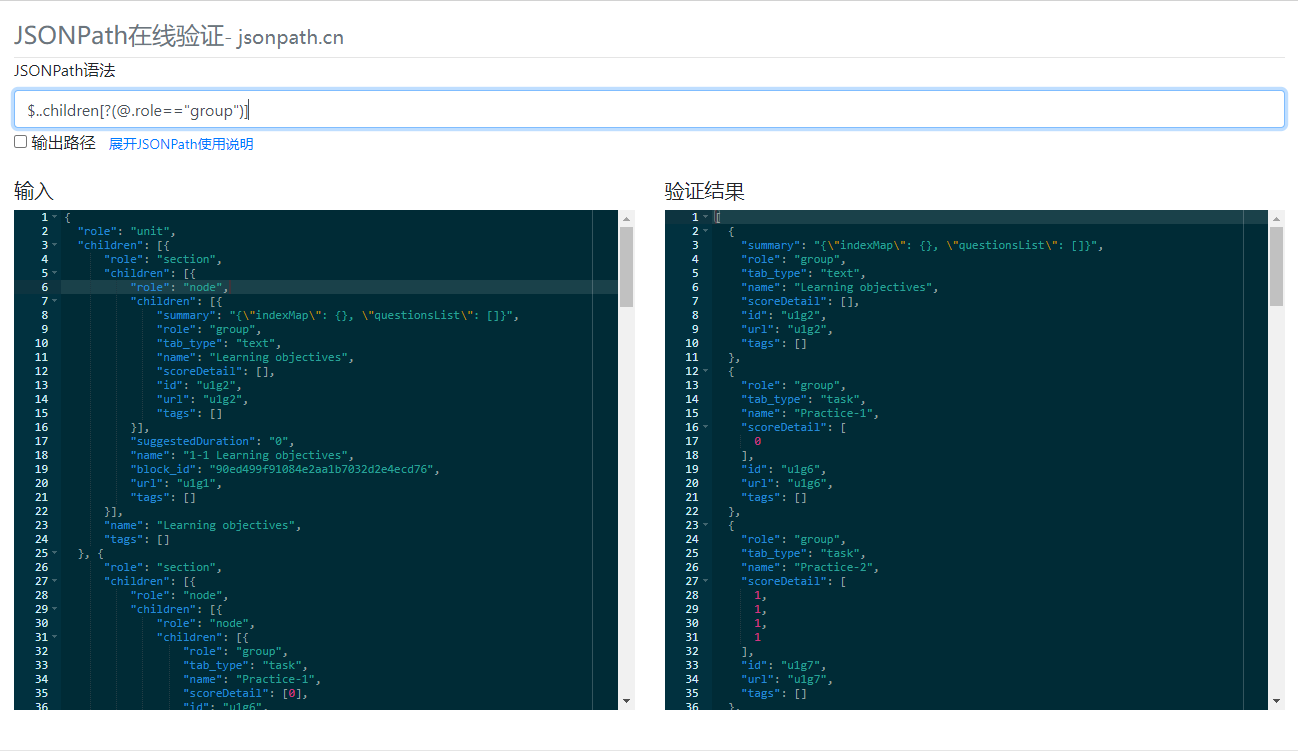
语法:$..children[?(@.role=="group")]
语法意思很明确,根节点下遍历所有children节点,同时role等于group,呈现的效果如上图。
而回到需求,就是获取role为group的children节点数据,而 jsonpath 就帮我轻松实现我想要的效果。
最终思考
实际上这样的需求我已经不止遇到一次,二次了,然而我寻求百度与群友的时候,给我的结果都不尽人意。但都没有提及到 jsonpath 来进行获取。也许是我的搜索方式有问题,但千篇一律都是 js 如何解析多层 json,以及遍历所有的子元素,虽然这些办法确实能解决我的问题,但每次遇到这种数据,都需要花上长时间去编写对应的逻辑。
在回想起当时爬取 HTML 页面数据的时候(数据与上面展示的差不多,都是树结构多层),而我只接触到了正则表达式,没了解过 CSS 选择器与 xpath。怎么办,为了实现目的,只好用现有的技术去实现,于是编写一个正则表达式就花费了近一个下午的时间,而使用 CSS 选择器 10 分钟不到就达到目的。没想到竟然有这么好用的方法,早知道多去了解点技术了。可能现在的心情和当时一样,只不过 HTML 换成了 JSON,编辑器还是那个编辑器,而我依旧还是我
也许这就是编程,也许这就是人生。